The sensation of discomfort, soreness, or aches in the body’s joints is a common issue affecting many individuals worldwide. Joint pain is more than an inconvenient symptom; it can significantly interfere with daily activities and overall quality of life. This article aims to unpack the topic of aching joints, providing an understanding of its causes and potential solutions. The discussion will delve into the anatomy of joints, explore the causes of joint discomfort, identify commonly affected joints, explain diagnostic methods, detail treatment options, and provide preventative measures for healthier joints.
Contents
Anatomy of Joints

The human body is an intricate system, and joints are essential. They connect bridges between bones, allowing smooth movement and providing stability. Joints are comprised of various elements, including cartilage, synovium, ligaments, and tendons, all working together to facilitate pain-free movement.
Understanding the structure of a joint is crucial to comprehending why joint pain occurs. They are subject to immense strain as they bear the body’s weight and enable mobility. When any part of a joint – the cartilage, the synovium, or the ligaments – becomes affected by injury or disease, it can result in the discomfort we recognize as joint pain.
Understanding Joint Pain
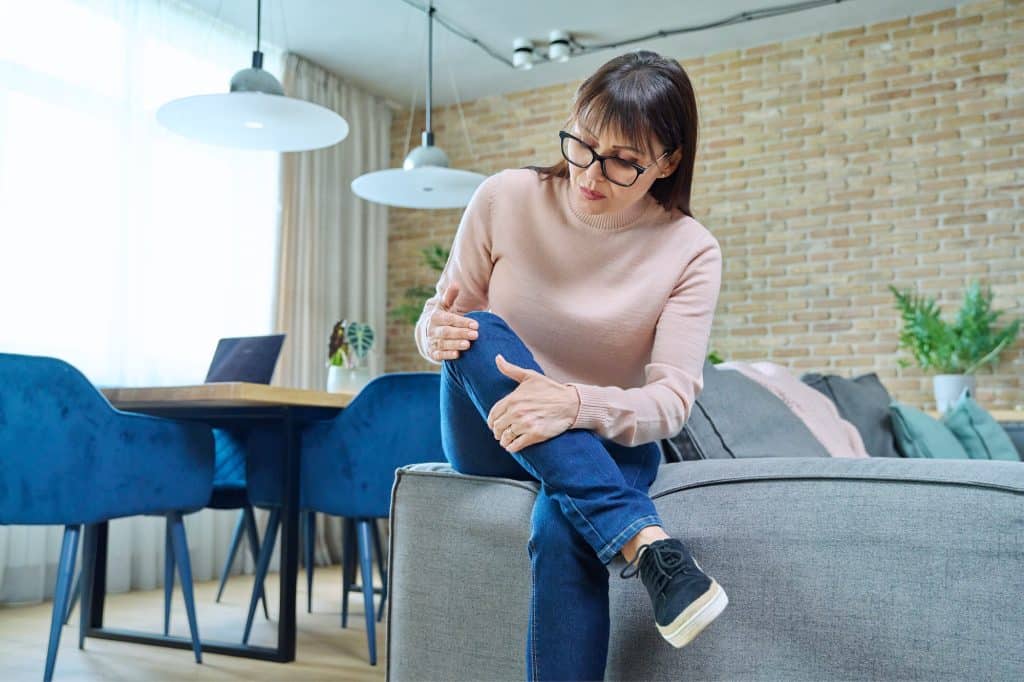

Joint pain is typically described as discomfort or inflammation arising from any part of a joint, including cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons, or muscles. It can range from mild irritations barely noticeable to severe, debilitating pain restricting movement.
Although joint pain is often associated with age-related conditions such as arthritis, it is crucial to remember that it is not exclusive to the elderly. People of all ages can experience joint pain from various conditions and lifestyle factors. Recognizing the variability in joint pain experiences is a key step in effective management and treatment.
Causes of Aching Joints

Joint pain can have many causes, with age being one of the most common factors. As individuals age, the wear and tear on the joints increase, leading to discomfort. Conditions such as osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease often seen in older adults, exemplify this type of age-related joint damage.
In addition to aging, joint pain can be triggered by various diseases and medical conditions. Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and gout are just some diseases that can cause inflammation and joint pain. Injuries can also cause immediate and long-term joint pain, depending on the severity and the body’s healing process. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can also contribute to joint pain by putting extra strain on the joints or leading to inflammatory responses in the body. Understanding these causes is an integral part of managing and alleviating joint pain.
Commonly Affected Joints
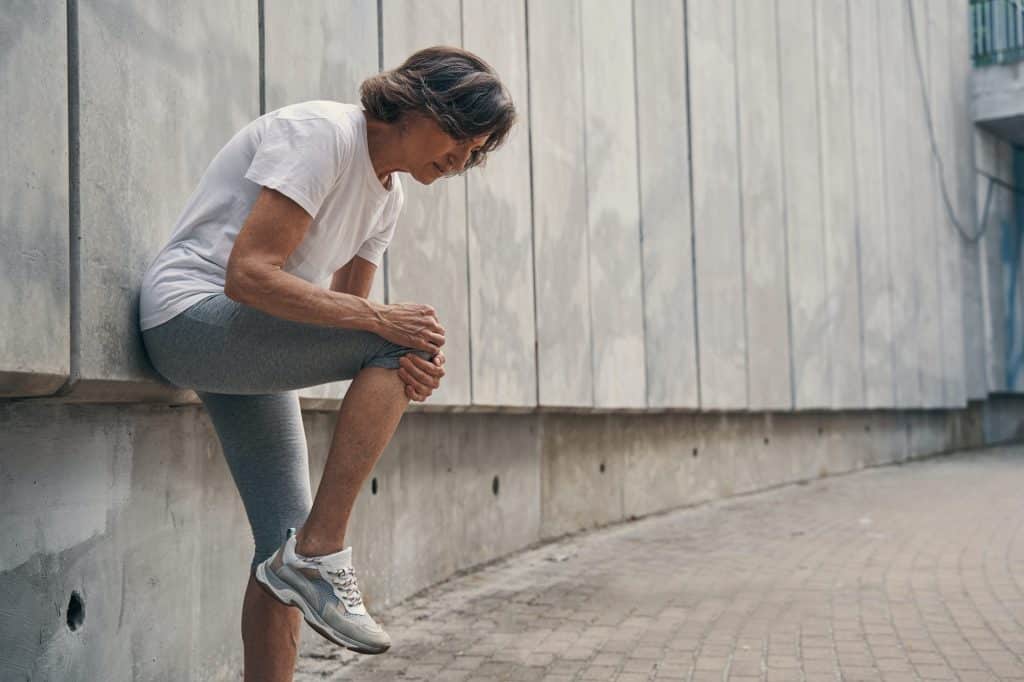

Certain joints in the body are more prone to pain and discomfort due to their function and the pressure they endure. The knee, for instance, is a weight-bearing joint that often falls victim to pain and discomfort. This joint’s intricate structure and heavy-duty role in standing and walking make it susceptible to injury and diseases like osteoarthritis.
Another common area of concern is the hip joint. Like the knee, the hip is a weight-bearing joint that is critical to mobility. It is frequently affected by conditions such as hip bursitis and arthritis. Meanwhile, smaller joints, such as those in the hands and wrists, are not spared either. Despite their size, these joints are pivotal for tasks requiring dexterity, and conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis can cause significant discomfort and pain.
Diagnosing Joint Pain

Diagnosing the cause of joint pain typically begins with an analysis of the patient’s medical history and a thorough physical examination. Healthcare professionals look at the symptoms, the affected joint’s location and characteristics, and any correlating events like injuries or the presence of disease.
For a more detailed view of the joint, imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasounds might be conducted. These tests can reveal issues like fractures, injuries to soft tissues, or signs of degenerative diseases. In certain cases, blood or other lab tests may be used to identify diseases that can cause joint pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis or infections. Proper diagnosis is the key to identifying the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Aching Joints
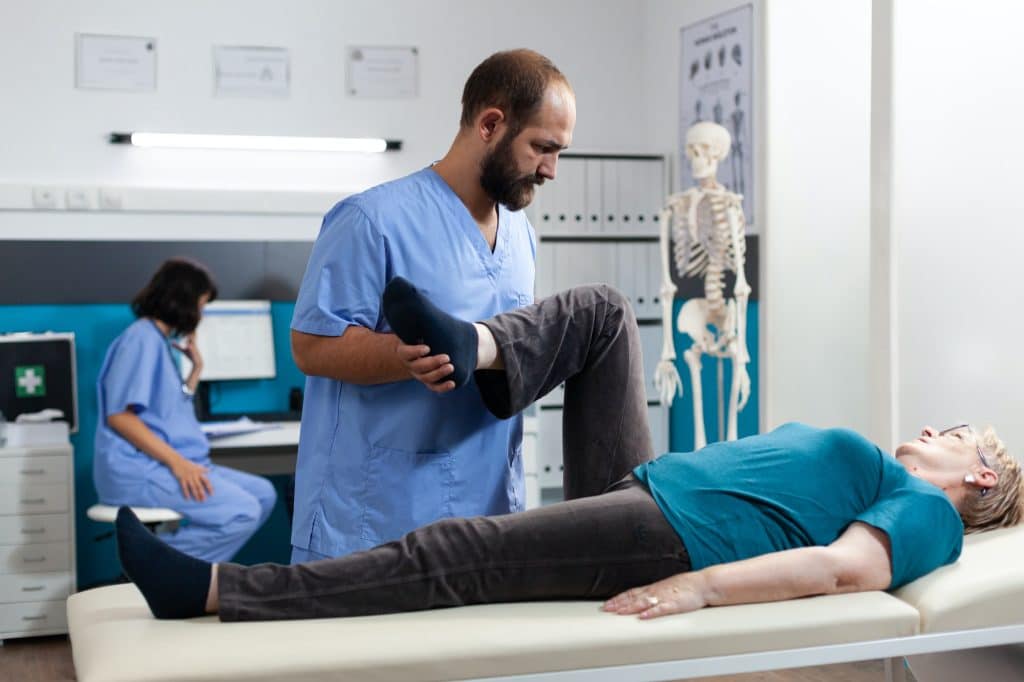
Once a diagnosis has been made, treatment can be prescribed based on the cause and severity of the joint pain. Non-pharmacological treatments often include physical therapy and exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the joint and relieve pressure. A weight loss regimen is recommended for overweight individuals to lessen the burden on weight-bearing joints.
When necessary, over-the-counter or prescription medications might be administered to manage the pain. These can range from topical creams to oral medication or even injections in severe cases. Surgical interventions like joint replacement or arthroscopy might be necessary in cases of advanced joint degradation or severe injury. In some situations, alternative treatments like acupuncture, massage therapy, or dietary supplements may also prove beneficial.
Preventing Joint Pain

Preventing joint pain involves leading a healthy lifestyle to maintain joint health. Regular exercise keeps joints flexible and strengthens the muscles supporting them, while a balanced diet ensures that the body gets the necessary nutrients to maintain healthy joints. Maintaining a healthy weight can also help by reducing stress on weight-bearing joints.
Along with these steps, regular medical check-ups can play a crucial role in preventing severe joint pain. Early diagnosis of potential issues often leads to more effective treatment and can prevent further deterioration of joint health. Prevention and early intervention can make a significant difference in managing and even avoiding joint pain.
The Bottom Line
Joint pain can be a debilitating condition that greatly impacts an individual’s daily life and overall quality of life. However, individuals are better equipped to manage and potentially prevent such discomfort by understanding the basic anatomy of joints, the various causes of aching joints, the common sites of occurrence, and the potential treatment options. Remember, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for persistent joint pain, as early diagnosis and treatment can often prevent further deterioration. Taking proactive steps towards joint health can significantly improve well-being and daily life quality.


