Across the globe, a deeper understanding of the leading causes of death sheds light on the health challenges faced by society. It emphasizes the necessity of early detection and preventive measures. This knowledge equips individuals to make informed decisions about their health, fostering a proactive community rather than a reactive one.
Contents
Cardiovascular Diseases

Cardiovascular diseases, often synonymous with heart diseases, encompass a range of conditions that include coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. These conditions often lead to heart attacks and strokes, making them a prominent cause of death worldwide. According to global statistics, they remain at the top of the list, owing in part to the modern sedentary lifestyle, genetic predispositions, and other risk factors.
Tackling cardiovascular diseases requires a two-pronged approach: prevention and management. On the one hand, preventive measures such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco can make a significant difference. On the other, early detection, regular health check-ups, and following medical advice can reduce the severity of these diseases.
Cancers

Cancer, an often feared term, is characterized by the uncontrollable growth of cells in the body. Various forms of cancer, including those of the lung, breast, and colon, have led to countless deaths. With risk factors ranging from genetics to environmental exposures, its complexity poses challenges for both prevention and treatment.
However, hope is far from lost. The advent of medical advancements has emphasized the role of early detection in improving survival rates. Regular screenings, self-examinations, and being aware of familial histories are steps in the right direction. Moreover, lifestyle changes, including avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol, and maintaining a balanced diet, can play pivotal roles in cancer prevention.
Respiratory Diseases

Respiratory diseases like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and asthma primarily affect the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system. Smoking remains the most dominant cause, but other factors like air pollution and occupational hazards also contribute significantly to the onset and progression of these diseases.
Early diagnosis is paramount for effective management of respiratory diseases. Regular medical check-ups, being aware of symptoms like persistent coughing or shortness of breath, and avoiding smoking can drastically reduce the toll of these diseases. Additionally, awareness campaigns highlighting the dangers of smoking and promoting cleaner air can mitigate the widespread effects of respiratory conditions.
Diabetes
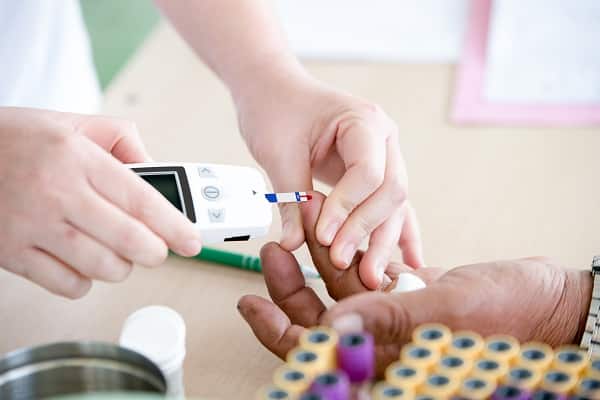
Diabetes, a condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin or fails to use it effectively, has been on a relentless rise globally. This metabolic disease can lead to a host of complications, including kidney damage, heart disease, and even vision loss, if not properly managed. Lifestyle choices, genetics, and environmental factors are among the leading contributors to its onset.
Prevention and management are key to combating the diabetic epidemic. Regular screenings, especially for those with a family history of the disease, are essential. Furthermore, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining an optimal weight can both prevent and help manage the condition, thereby reducing the associated life-threatening complications.
Alzheimer’s Disease and other Dementias

Alzheimer’s Disease, the most common form of dementia, is a progressive condition that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. With an aging global population, the number of individuals affected by Alzheimer’s and other dementias is on the rise. Beyond the direct impact on patients, these conditions also place immense emotional and financial stress on caregivers and families.
Addressing the challenge of Alzheimer’s requires comprehensive medical research to find effective treatments. Meanwhile, early detection and supportive care play crucial roles in managing the disease. Communities and families can also benefit from awareness campaigns that provide resources, support systems, and coping mechanisms to those affected.
Infectious Diseases
From the flu to HIV/AIDS, infectious diseases have historically posed major health threats. Recent times have witnessed the emergence and re-emergence of infectious diseases, some leading to global pandemics. While medical advancements have curtailed many infectious agents, changing ecosystems, urbanization, and global travel have paved the way for new challenges.
Vaccination remains the most potent weapon against many infectious diseases. Emphasizing the importance of vaccines, maintaining proper hygiene, and fostering global cooperation in disease surveillance can prevent outbreaks and reduce mortality rates. Public health systems also play an indispensable role in early detection, containment, and treatment.
Kidney Diseases

Kidney diseases, often silent killers, can be attributed to conditions like hypertension and diabetes. The kidney’s role in filtering blood makes it essential for overall health, and its impairment can have dire consequences, ranging from waste build-up to complete kidney failure.
Early detection and proper management can reduce the severity of kidney diseases. Regular health check-ups, especially for those with risk factors, are vital. Besides medical interventions, lifestyle changes such as reducing salt intake, avoiding over-the-counter pain medications, and monitoring blood pressure can prevent and manage kidney-related conditions.
Accidents and Unintentional Injuries

Unintentional injuries, from car accidents to falls, are unpredictable yet account for a significant number of deaths globally. Factors like high-speed driving, substance abuse, and unsafe environments increase the risk of these tragedies.
Promoting safety measures and creating stringent regulations can reduce the occurrence of such accidents. Public awareness campaigns on safe driving, the importance of safety equipment, and the perils of driving under the influence can make a considerable difference. Individuals can also take proactive steps like childproofing homes and adhering to safety guidelines at workplaces.
Liver Diseases

Liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, affect a significant portion of the global population. Chronic alcohol consumption, hepatitis infections, and fatty liver disease are among the top contributors. The liver’s pivotal role in digestion, detoxification, and metabolism means its impairment can have wide-ranging effects on health.
Regular health screenings, especially for at-risk populations, can aid in early detection and treatment. Moreover, abstaining from excessive alcohol, being cautious with medications, and ensuring protection against hepatitis viruses can keep liver diseases at bay.
The Bottom Line
Understanding the top health-related causes of death provides more than mere statistics; it offers a roadmap for individuals and communities to channel efforts toward prevention, early detection, and improved care. Embracing a proactive approach, underpinned by awareness and access to medical facilities, can sculpt a future where these causes become less menacing and more manageable.


