Sleep isn’t just a nightly ritual; it’s a cornerstone of good health. Yet, many people overlook the significance of their sleeping position, focusing instead on the duration or quality of their slumber. This article aims to shed light on the various sleeping positions and their health implications. From spinal alignment to the risk of sleep apnea, the way you sleep can have a profound impact on your well-being. So, let’s embark on a journey to discover whether your sleeping position is contributing to a healthier you or if it’s time for a change.
Contents
- The Science Behind Quality Sleep
- The Supine Position (Sleeping on Your Back)
- The Prone Position (Sleeping On Your Stomach)
- The Fetal Position (Curled Up)
- The Lateral Position (Sleeping On Your Side)
- The Rotator (Changing Positions Frequently)
- How To Choose The Right Sleeping Position
- Find Your Perfect Position For Healthier Sleep!
- Related
The Science Behind Quality Sleep

Understanding the mechanics of sleep is crucial for evaluating the impact of sleeping positions on your health. Sleep is not a monolithic state but a series of cycles, each with its own physiological characteristics. These cycles include stages like light sleep, deep sleep, and REM sleep, which play different roles in physical and mental restoration. Your sleeping position can affect how smoothly you transition between these stages, thereby influencing the overall quality of your sleep.
The position you choose to sleep in can also have immediate health effects. For instance, some positions may alleviate back pain, while others could exacerbate issues like acid reflux or sleep apnea. Knowing the science behind sleep can empower you to make informed decisions about your sleeping habits, setting the stage for a closer look at individual positions.
The Supine Position (Sleeping on Your Back)

Sleeping on your back or in the supine position is often touted as the go-to choice for spinal health. When you lie on your back, your spine is in a neutral position, which minimizes the risk of developing back pain. This position also allows for better weight distribution, reducing the likelihood of pressure sores. Moreover, back sleeping can help in reducing acid reflux, especially if your upper body is slightly elevated.
However, it’s not all sunshine and rainbows. The supine position is infamous for being a significant contributor to snoring and, in more severe cases, obstructive sleep apnea. When you sleep on your back, the base of your tongue and soft palate collapse to the back of your throat, obstructing the airway. This can lead to snoring and interrupted breathing, which are not only annoying but also potentially dangerous health concerns.
The Prone Position (Sleeping On Your Stomach)

For some, sleeping on the stomach feels incredibly comfortable, but is it healthy? This position can actually help reduce snoring since it keeps the upper airways more open than back sleeping. Some people also find that it alleviates some types of lower back pain, although this is not universally true.
On the flip side, the prone position can be a nightmare for your neck and spine. When you sleep on your stomach, your neck is twisted to the side to allow for breathing, putting immense strain on the neck muscles and vertebrae. This awkward angle can lead to chronic pain and discomfort over time. Additionally, stomach sleeping can put pressure on internal organs, which is another point to consider when evaluating its health implications.
The Fetal Position (Curled Up)
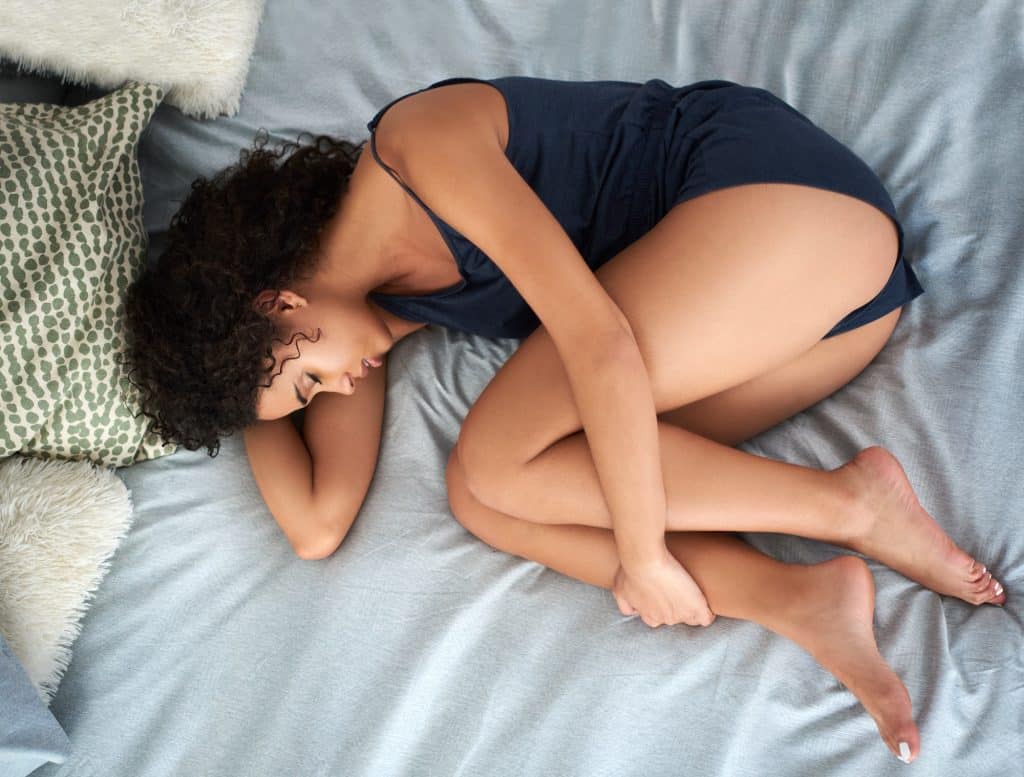

The fetal position, where you sleep curled up with your knees drawn towards your chest, is a common choice for many. It’s a position that mimics the natural posture of humans in the womb, offering a sense of comfort and security. This position can also be beneficial for reducing snoring and is often recommended for pregnant women, as it improves circulation to the fetus and prevents the uterus from pressing against the liver.
However, the fetal position isn’t without its drawbacks. Curling up too tightly can restrict your diaphragmatic breathing, leading to reduced oxygen intake. It can also put a strain on your hips and knees, potentially causing joint pain and stiffness over time. If you already suffer from arthritis or joint issues, this position may exacerbate your symptoms.
The Lateral Position (Sleeping On Your Side)
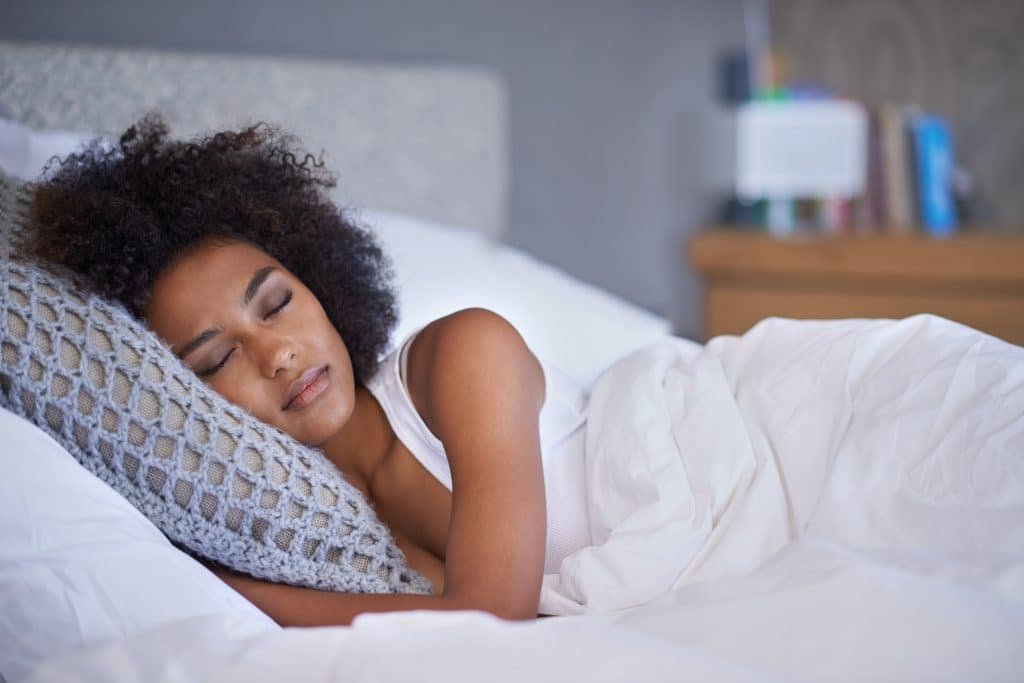

Side sleeping, also known as the lateral position, is another popular choice and comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. One of the significant benefits of sleeping on your side is spinal alignment. When done correctly, with a pillow that supports the neck and head, this position can help maintain a straight and natural spinal posture. Side sleeping can also be beneficial for those who suffer from acid reflux and heartburn, especially when lying on the left side.
However, the lateral position can sometimes lead to shoulder pain due to the pressure exerted on the lower shoulder. This is particularly true for people who remain in the same side position throughout the night. Additionally, sleeping on your side can cause wrinkles and may contribute to skin aging, as one side of your face is pressed against the pillow for extended periods.
The Rotator (Changing Positions Frequently)

For those who find themselves frequently changing positions throughout the night, you’re not alone. This approach has its own set of benefits, including a reduced risk of developing pressure sores, as the weight and pressure on your skin are distributed more evenly. Frequent position changes can also alleviate minor discomforts and restlessness, making it easier to fall back asleep if you wake up during the night.
However, constantly changing your sleeping position can disrupt your sleep cycle, making it difficult to reach the deeper, more restorative stages of sleep. This could lead to sleep fragmentation, where you wake up multiple times during the night, affecting the overall quality of your sleep. It may also increase the likelihood of sleep disorders like insomnia.
How To Choose The Right Sleeping Position

Choosing the proper sleeping position is not a one-size-fits-all decision; it often requires some experimentation. Factors such as existing health conditions, comfort preferences, and even your partner’s sleeping habits can all play a role. For instance, people with chronic back pain may find relief in certain positions but not others. Similarly, those with sleep apnea may need to avoid back sleeping altogether.
Medical professionals and sleep experts can offer valuable insights into choosing the best sleeping position for you. They may recommend specific positions based on your health profile or even suggest using specialized pillows or sleep aids to improve your sleep quality. Ultimately, the goal is to find a position that allows for a good night’s sleep while minimizing any adverse health effects.
Find Your Perfect Position For Healthier Sleep!
Understanding the pros and cons of various sleeping positions can be a game-changer for your overall well-being. While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, being informed allows you to make better choices tailored to your specific needs. Don’t underestimate the power of a good night’s sleep. Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and consider making adjustments to your sleep posture. Your body and mind will thank you!