Dementia, a term that strikes fear and confusion in the hearts of many, is a collective name for the loss of memory, language, problem-solving, and other thinking abilities significant enough to interfere with daily life. Characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive functions, it’s not a single disease but rather a series of symptoms associated with multiple disorders. It affects millions worldwide, not only impacting those living with it but also their families and caregivers. Exploring ways to mitigate its onset and progression is paramount. This post delves into various strategies, grounded in scientific research, to combat dementia effectively.
Contents
Understanding Dementia

Dementia is characterized by a decline in mental abilities, impacting an individual’s daily life and independence. Memory loss is a common symptom, but dementia also affects communication, attention, and reasoning. Various types, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia, each come with distinct symptoms and challenges. Early detection and diagnosis can be pivotal in managing the disease’s progression and mitigating its impact on the affected individual and their loved ones.
Risk factors for dementia can be genetic or related to lifestyle and environmental influences. Age is a significant factor; however, it is not an inevitable part of aging. Addressing modifiable risk factors such as hypertension, obesity, and diabetes can be instrumental in reducing the risk of dementia. Educational and awareness programs aim to inform the public about these aspects, emphasizing preventive measures that are within one’s control to modify.
Brain-Healthy Diet
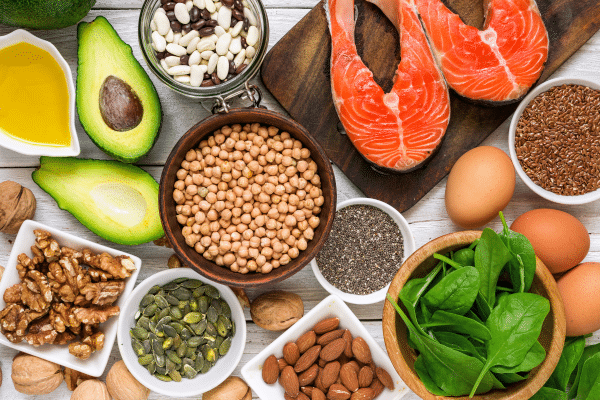

Nutrition plays a critical role in overall brain health and can influence the risk and progression of dementia. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports cognitive function. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are particularly beneficial. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins also contribute to a brain-healthy diet, offering a range of nutrients essential for optimal brain function.
Adopting specific dietary patterns can further support brain health. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been associated with a reduced risk of cognitive decline. Similarly, the DASH diet, designed to combat hypertension, has shown promise in promoting brain health. Incorporating these dietary principles can make a significant difference in enhancing cognitive resilience and reducing the risk of dementia.
Physical Activity And Exercise

Engaging in regular physical activity is integral to maintaining cognitive health and can potentially reduce the risk of developing dementia. Exercises, especially those that elevate the heart rate, increase blood flow to the entire body, including the brain. This enhanced circulation aids in delivering essential nutrients and oxygen, supporting optimal brain function. Moreover, exercise stimulates the release of chemicals that foster brain cell health, promote the growth of new blood vessels in the brain, and even enhance the abundance and survival of new brain cells.
A mix of different types of exercises can be particularly beneficial. Cardiovascular exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling boost heart health and increase blood flow. Strength training helps in maintaining muscle mass and bone density, while flexibility and balance exercises can reduce the risk of falls. Incorporating a variety of these activities into a weekly routine can contribute significantly to both physical and cognitive well-being.
Mental Stimulation And Cognitive Reserve
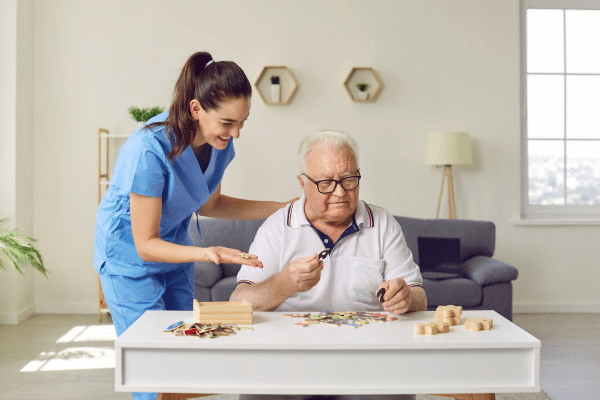

Keeping the brain actively engaged and challenged can enhance its functioning and resilience. Activities such as reading, solving puzzles, or learning new skills can stimulate the brain and strengthen the connections between nerve cells. Such mental exercises increase the brain’s cognitive reserve, which refers to its ability to improvise and find alternative ways of performing tasks, especially useful when aging or disease affects normal cognitive functioning.
Research has shown that individuals with higher cognitive reserves can better manage the symptoms of dementia. This is attributed to their brain’s ability to adapt and utilize alternative pathways for processing information. Building cognitive reserve can start at any age, with lifelong learning and intellectual curiosity serving as pillars for enhancing cognitive resilience and delaying the onset of dementia symptoms.
Social Engagement
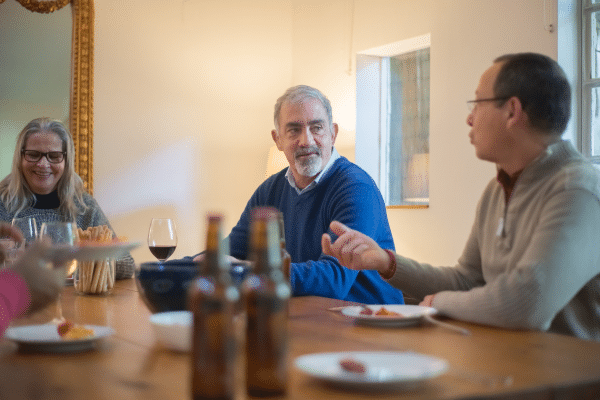

Being socially active and maintaining interpersonal relationships can have a positive impact on mental health. Engaging in social activities stimulates brain regions involved in emotional regulation and cognitive processing. It provides opportunities for learning, problem-solving, and emotional exchange, all of which contribute to cognitive resilience. People who are socially active are less likely to experience cognitive decline compared to those who remain isolated.
Social engagement also provides emotional support, reducing stress and depression, factors known to contribute to cognitive decline. Activities that combine both social and mental elements, such as joining clubs or groups related to hobbies, volunteering, or participating in community services, not only enrich the emotional well-being but also stimulate cognitive activities. Each social interaction contributes to the strengthening of brain networks, thus building a buffer against cognitive decline.
Sleep And Stress Management
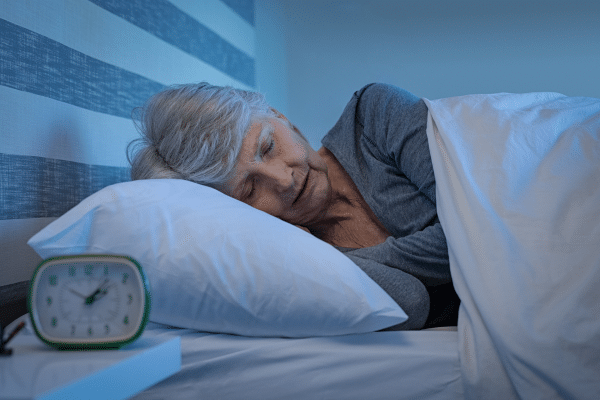

Adequate sleep is indispensable for cognitive health, playing a pivotal role in the consolidation of memories and learning. Sleep disturbances or chronic deprivation can lead to cognitive deficits, impacting attention, long-term memory, and decision-making. Establishing a healthy sleep routine and addressing sleep-related issues can significantly contribute to reducing the risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) have proven effective in improving sleep quality.
Similarly, managing stress is integral to promoting cognitive well-being. Chronic stress, characterized by prolonged exposure to stressors, can lead to adverse effects on the brain, including the reduction of the brain’s capacity to resist damage and adapt to challenging situations. Methods like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and participation in enjoyable activities can mitigate stress effects, fostering a brain environment conducive to cognitive preservation and enhancement.
Medical Check-ups And Treatments
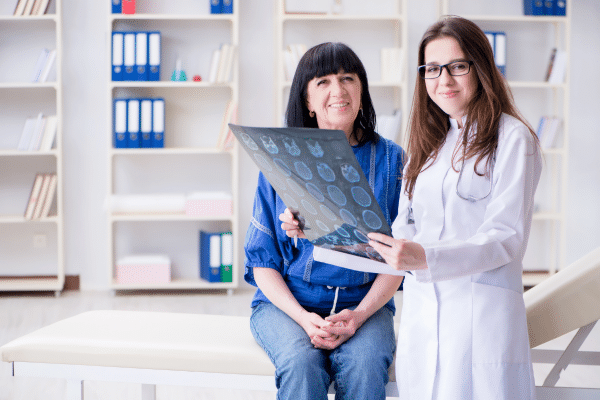

Regular medical check-ups are essential in monitoring overall health, especially as individuals age. These evaluations can identify potential health issues before they escalate, including those that increase the risk of dementia, such as hypertension, diabetes, or high cholesterol. Addressing these concerns promptly ensures better management and control, indirectly contributing to cognitive health preservation.
Regarding treatments for dementia, advancements are continually emerging. Medications can sometimes manage symptoms, and non-pharmaceutical interventions like cognitive therapy can also be beneficial. It’s crucial for individuals and caregivers to be informed about the latest treatment options and to work closely with healthcare providers to devise individualized management plans tailored to the specific needs and progression of the condition.
The Bottom Line
In the journey to combat dementia, a multifaceted approach incorporating a balanced diet, regular physical activity, mental stimulation, social engagement, quality sleep, and stress management proves essential. Each element plays a distinct role in promoting cognitive resilience and well-being. Additionally, regular medical check-ups and staying informed about treatment advancements enhance the capacity to manage and mitigate the effects of this condition. With these strategies, enhancing quality of life and cognitive health becomes an attainable goal for many, fostering a future where dementia’s impact is significantly reduced.