The global rise in diabetes cases is more than just a statistic; it’s a wake-up call for everyone to take this health issue seriously. With over 422 million people affected worldwide, diabetes is no longer a condition that one can afford to ignore. Understanding this complex ailment is crucial, not just for those who are diagnosed but also for their families and communities. This article aims to be your comprehensive guide to diabetes, covering everything from its basic fundamentals to treatment options and ongoing management. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, a long-term patient, or someone looking to educate themselves, this post offers valuable insights.
Contents
The Fundamentals Of Diabetes
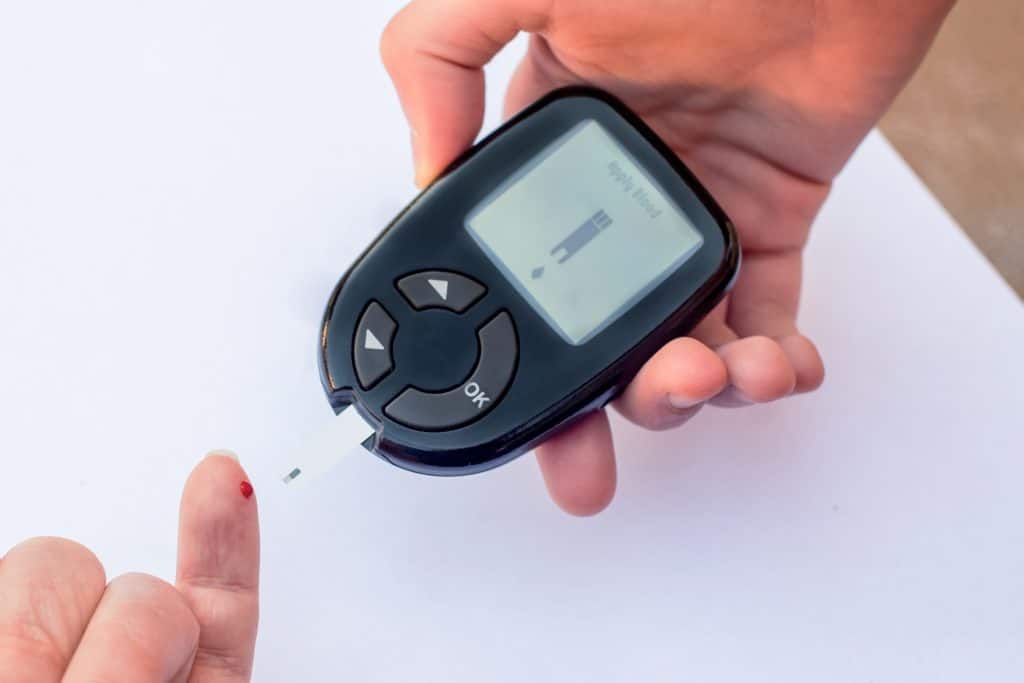

Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, also known as glucose. The body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar or can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes. Type 1 is usually diagnosed in children and young adults and is characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin. Type 2, the most common form, occurs when the body can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth.
The prevalence of diabetes is staggering, with millions of new cases diagnosed each year. According to the World Health Organization, the number of people with diabetes has nearly quadrupled since 1980. This rise is not just a concern for the healthcare system but also poses a significant public health risk. Early diagnosis is crucial, as untreated diabetes can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Recognizing The Symptoms
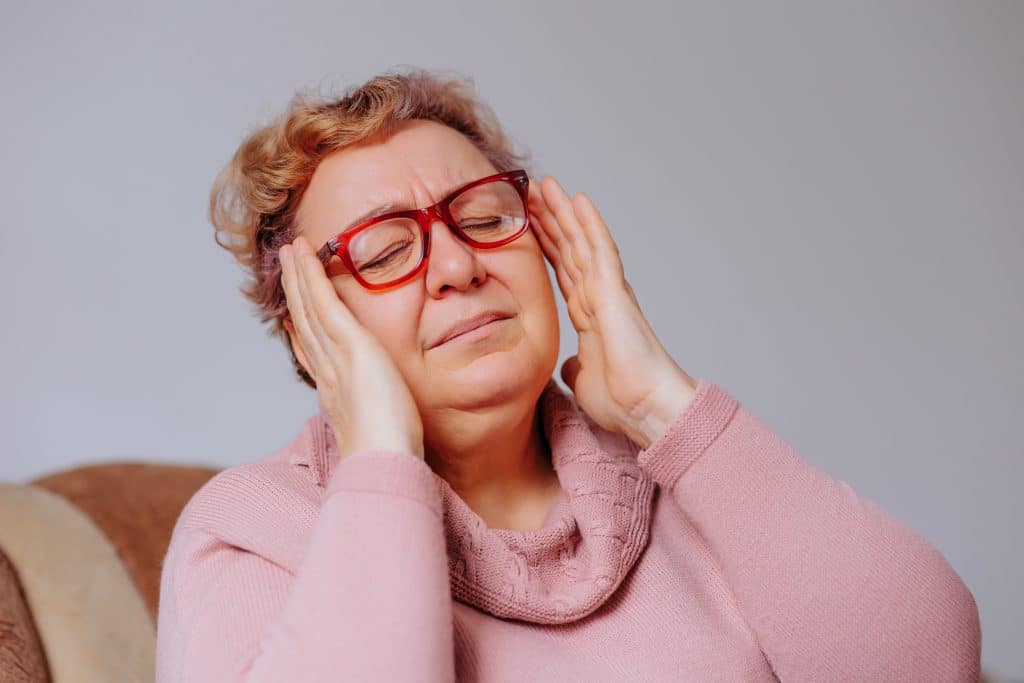

The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained fatigue. These symptoms often appear subtly and may be easy to dismiss as mere quirks or temporary phases. However, ignoring these signs can have severe consequences, as early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Less common symptoms include blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, and frequent infections. These symptoms are often more prevalent in the later stages of diabetes and can indicate that the condition has progressed to a more severe state. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Blood tests and other diagnostic measures can confirm whether or not you have diabetes.
Diagnosis And Tests
Diagnosis of diabetes typically involves a series of blood tests. The most common tests are the fasting plasma glucose test and the A1C test, which measures your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. These tests are usually conducted after an overnight fast and can provide a clear indication of whether or not you have diabetes. Some healthcare providers may also recommend an oral glucose tolerance test, especially for diagnosing gestational diabetes.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective diabetes management. If left untreated, the condition can lead to a host of complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and even blindness. Once diagnosed, the next step is to explore treatment options, ranging from medication and lifestyle changes to alternative therapies. The goal is to manage blood sugar levels effectively to prevent complications.
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating diabetes, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may include a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes alternative therapies. Medication is usually the first line of treatment, especially for Type 1 diabetes, where insulin injections are essential. For Type 2 diabetes, oral medications like Metformin are commonly prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle changes are equally important in managing diabetes effectively. A balanced diet rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats can go a long way in controlling blood sugar levels. Regular exercise is another crucial component, as it helps improve insulin sensitivity and promotes overall well-being. Some people also explore alternative therapies like herbal remedies and acupuncture, although these should be discussed with a healthcare provider for their efficacy and safety.
Managing Diabetes Day-To-Day
Managing diabetes is a daily commitment that involves more than just taking medication. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is essential for understanding how different factors like food, exercise, and stress affect your condition. Many people use glucose meters to check their blood sugar levels at home, while continuous glucose monitoring systems offer a more comprehensive view.
Diet plays a pivotal role in diabetes management. Foods high in sugar and simple carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar levels and should be avoided. Instead, focus on a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Exercise is another key element; even a simple 30-minute walk each day can make a significant difference. The objective is to create a sustainable routine that helps manage blood sugar levels effectively, thereby reducing the risk of complications.
Complications Of Unmanaged Diabetes

Unmanaged diabetes can lead to a host of complications that can severely impact your quality of life. In the short term, you may experience episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), both of which require immediate attention. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms like shakiness, confusion, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Hyperglycemia, on the other hand, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition.
Long-term complications are even more concerning. Persistent high blood sugar levels can damage various organs and systems in your body, leading to heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss, among others. Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is another common complication that can result in loss of sensation in the extremities. These complications underscore the importance of effective diabetes management and the need for a strong support system.
Building A Support System
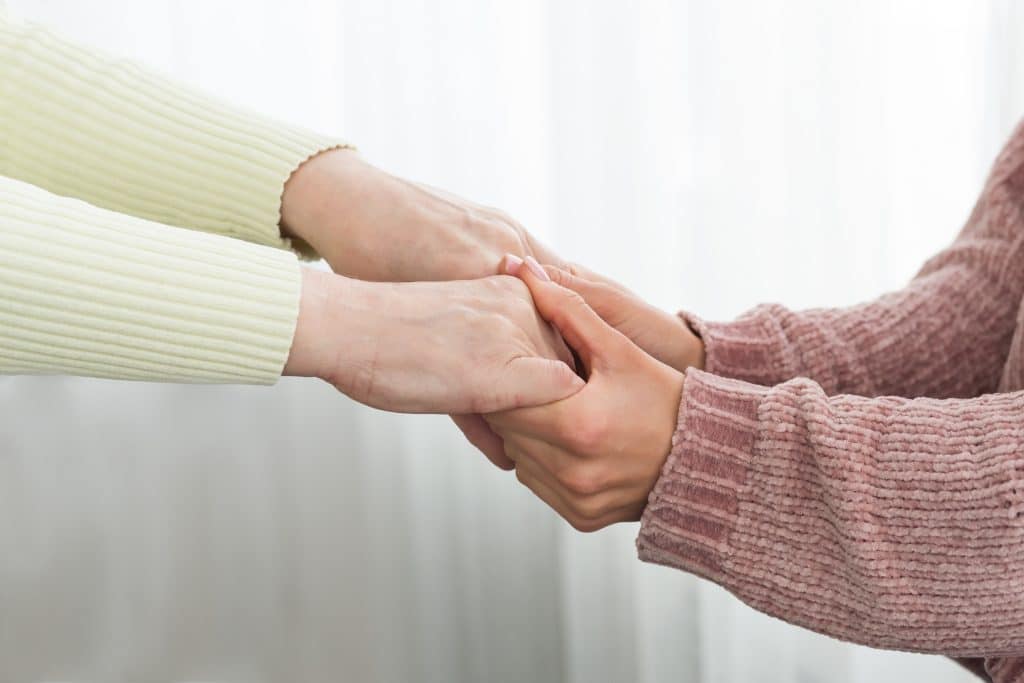

Living with diabetes can be challenging, but you don’t have to go it alone. A strong support system can make a significant difference in how effectively you manage your condition. Family and friends can offer emotional support, helping you stick to your treatment plan and make healthier lifestyle choices. They can also assist in practical ways, such as accompanying you to medical appointments or helping you monitor your blood sugar levels.
In addition to your personal network, your medical team plays a crucial role in your diabetes management. Regular check-ups and consultations are essential for monitoring your condition and making any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Online communities and support groups can also provide valuable insights and emotional support. Connecting with others who are going through similar challenges can offer a sense of community and help you navigate the complexities of living with diabetes.
Take The First Step In Your Diabetes Journey
In a world where diabetes is increasingly prevalent, awareness and education are your best defenses. This article has provided a comprehensive guide to understanding this complex condition, from recognizing symptoms and getting diagnosed to managing it effectively and building a solid support system. While the journey may be challenging, remember that you’re not alone. Take the first step today—whether it’s getting tested, consulting a healthcare provider, or making lifestyle changes. Your health is worth it.