Inflammation is a natural body response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Diet plays a crucial role in managing inflammation, and certain vegetables offer anti-inflammatory benefits that can help mitigate the risks associated with chronic inflammation. This article aims to explore various vegetables that are not only nutritious but also possess anti-inflammatory properties. From leafy greens like spinach to root vegetables like beets, the focus will be on how these veggies can be a valuable addition to a balanced diet to fight inflammation.
Spinach

Spinach is a leafy green vegetable rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals such as iron, calcium, and magnesium. These nutrients make it an excellent choice for a healthy diet. The vegetable contains compounds like quercetin, which has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Quercetin works by inhibiting the inflammatory processes in the body, making spinach a good option for those looking to manage inflammation through diet.
Incorporating spinach into one’s diet is relatively easy due to its versatility. It can be added to smoothies for a nutrient boost, used in salads for a fresh, leafy component, or cooked into dishes like omelets and casseroles. Whether raw or cooked, spinach retains its nutritional value, making it a convenient and beneficial addition to meals.
Broccoli

Broccoli is another vegetable that packs a nutritional punch. It is rich in vitamins K and C and fiber, making it beneficial for digestive health. Moreover, broccoli contains sulforaphane, a compound that has been found to have potent anti-inflammatory effects. Sulforaphane targets inflammation at the cellular level, making broccoli a valuable vegetable for those looking to manage inflammation.
Adding broccoli to the diet can be as simple as steaming it for a side dish or incorporating it into stir-fries. It can also be roasted with a drizzle of olive oil and some seasoning for a delicious and nutritious snack. The key is avoiding overcooking it, which can diminish its nutritional value. Lightly steaming or roasting can help preserve the essential nutrients that make broccoli an anti-inflammatory powerhouse.
Bell Peppers

Bell peppers are not only colorful but also rich in nutrients. They are an excellent source of vitamin C, which is known for its immune-boosting properties. In addition to vitamin C, bell peppers contain capsaicin, a compound that has been shown to reduce markers of inflammation in the body. Capsaicin works by inhibiting the inflammatory pathways, making bell peppers an effective vegetable for combating inflammation.
Bell peppers are incredibly versatile and can be included in various dishes. They can be sliced and added to salads for color and flavor or cooked into dishes like fajitas and casseroles. They can also be stuffed with grains and proteins for a wholesome meal. Whether raw or cooked, bell peppers offer taste and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Beets
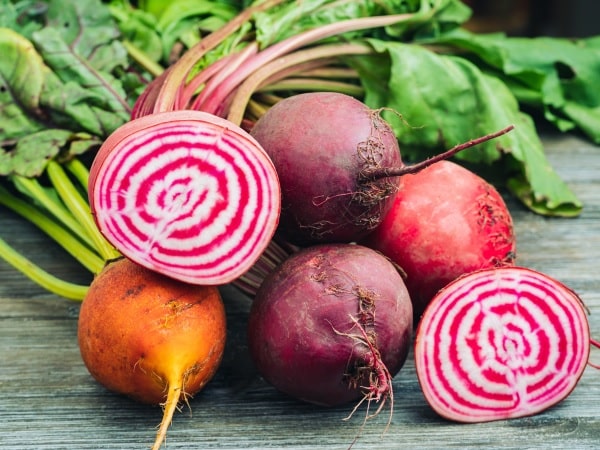

Beets are root vegetables known for their deep red color and earthy flavor. They are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals like potassium and manganese. One of the key compounds in beets is betalain, which has been found to offer anti-inflammatory benefits. Betalains neutralize enzymes in the body that trigger inflammation, making beets a useful vegetable for those looking to manage inflammatory conditions.
Incorporating beets into the diet can be as simple as adding them to juices or smoothies for an extra nutrient kick. They can also be roasted with a sprinkle of salt and pepper for a hearty side dish or sliced thinly and added to salads. The versatility of beets makes them an easy and effective way to add anti-inflammatory foods to any meal plan.
Carrots
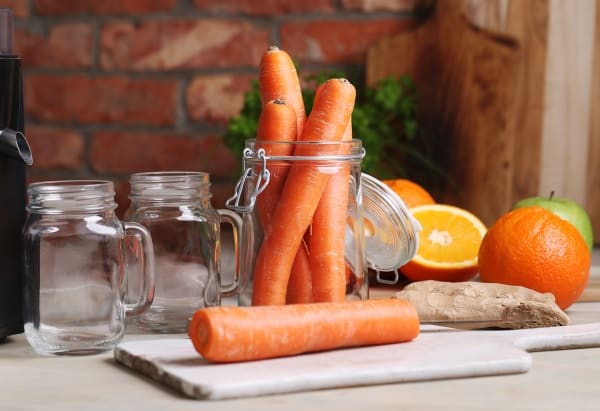

Carrots are a popular vegetable known for their vibrant orange color, although they come in various other hues like purple, yellow, and red. They are rich in beta-carotene, an antioxidant that converts to vitamin A in the body. Vitamin A plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation by regulating the immune system and inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Adding carrots to one’s diet is straightforward and can be done in numerous ways. They can be consumed raw as a crunchy snack, added to salads for a pop of color, or cooked into soups and stews. Carrots can be juiced with other fruits and vegetables for a nutrient-packed beverage. Their natural sweetness and versatility make them an easy addition to meals, offering flavor and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Sweet Potatoes

Sweet potatoes are starchy root vegetables rich in fiber, vitamins A and C, and minerals like potassium and manganese. They contain anthocyanins and other antioxidants that have been found to have anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds work by neutralizing free radicals in the body, thereby reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Incorporating sweet potatoes into the diet is easy and can be quite delicious. They can be baked and topped with a dollop of Greek yogurt for a healthy snack, mashed as a side dish, or used in casseroles for a hearty meal. The natural sweetness of sweet potatoes also makes them suitable for desserts, offering a healthier alternative to traditional sugary treats.
Garlic

Garlic is a pungent vegetable used commonly as a seasoning in various cuisines. It contains vitamins C and B6 and manganese and is known for its strong flavor and aroma. Garlic contains allicin, a compound found to have anti-inflammatory effects. Allicin works by inhibiting the activation of certain pathways that trigger inflammation, making garlic a potent anti-inflammatory food.
Adding garlic to meals is an easy way to boost flavor and health benefits. It can be minced and added to sauces, used to season meats and vegetables, or incorporated into stir-fries and casseroles. The key is to use it in moderation, as its strong flavor can overpower other ingredients. However, garlic can elevate a dish when used correctly while providing anti-inflammatory benefits.
Kale

Kale is a leafy green vegetable that has gained popularity for its high nutrient content. It is rich in vitamins A, K, and C and minerals like calcium and potassium. Kale contains flavonoids, compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory benefits. These flavonoids work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory markers, making kale a valuable addition to an anti-inflammatory diet.
Incorporating kale into the diet can be done in various ways. It can be used in salads, added to smoothies for a nutrient boost, or sautéed with a bit of olive oil and garlic for a tasty side dish. Its slightly bitter taste pairs well with sweet and savory ingredients, making it a versatile vegetable for various dishes.
The Bottom Line
The role of diet in managing inflammation cannot be overstated. Incorporating anti-inflammatory vegetables like spinach, broccoli, bell peppers, beets, carrots, sweet potatoes, garlic, and kale can offer a range of health benefits, from boosting the immune system to reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Each vegetable discussed in this article not only offers a unique set of nutrients but also contains specific compounds that have been found to have anti-inflammatory properties. Making these vegetables a regular part of a balanced diet can be a simple yet effective way to promote better health and well-being.