Antibiotics have revolutionized modern medicine, yet many aspects of these powerful drugs remain misunderstood or unknown to the general public. From their discovery to their complex mechanisms of action, antibiotics play a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. This post will delve into the history, types, workings, and common misconceptions surrounding antibiotics. By shedding light on these areas, you will gain a more comprehensive understanding of these essential medical tools.
Contents
History of Antibiotics

The history of antibiotics dates back to the early 20th century, with the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928. This accidental finding marked the beginning of a new era in medicine, allowing for the effective treatment of previously untreatable bacterial infections. Penicillin’s impact was so profound that it earned Fleming a Nobel Prize and paved the way for further antibiotic discoveries.
Following penicillin, various other antibiotics were developed, each targeting different types of bacteria. The introduction of antibiotics like streptomycin and tetracycline expanded the medical arsenal against infections. These discoveries not only improved patient outcomes but also shaped modern surgical practices, enabling more complex procedures by preventing post-surgical infections.
Types of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are classified into different types based on their spectrum of activity and the specific bacteria they target. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, can fight a wide range of bacteria, making them versatile in treating various infections. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics, on the other hand, are more specialized, targeting specific bacterial strains. Understanding these classifications helps healthcare providers prescribe the most effective treatment for each infection.
Beyond the spectrum of activity, antibiotics are also categorized by their chemical structure and mechanism of action. For example, beta-lactams, including penicillins and cephalosporins, disrupt bacterial cell walls, while macrolides like erythromycin inhibit protein synthesis within the bacteria. These classifications not only guide medical professionals in choosing the right antibiotic but also play a vital role in research and development, leading to the creation of new and more effective drugs.
How Antibiotics Work

Antibiotics function by targeting specific components of bacterial cells, thereby inhibiting their growth or killing them outright. Unlike antivirals, which target viruses, antibiotics are designed to combat bacterial infections. The mechanisms by which they achieve this are varied and fascinating, reflecting the complexity of bacterial organisms themselves.
Some antibiotics, such as penicillins, target the bacterial cell wall, causing it to weaken and eventually rupture. Others, like tetracyclines, interfere with the bacteria’s ability to produce essential proteins, effectively halting their growth. These targeted approaches allow antibiotics to be highly effective against bacterial infections without harming the body’s own cells.
Misuse Of Antibiotics

The misuse of antibiotics is a growing concern in healthcare, leading to a host of problems, including antibiotic resistance. Overprescription by healthcare providers and self-medication by patients without proper guidance contribute to this issue. When antibiotics are used unnecessarily or incorrectly, bacteria can develop resistance, rendering the drugs ineffective.
The impact of antibiotic misuse extends beyond individual health and affects public health on a global scale. Incomplete courses of antibiotics or using them for viral infections, where they have no effect, can lead to the emergence of superbugs. These resistant strains pose a significant threat, as they can spread rapidly and are challenging to treat, emphasizing the importance of proper antibiotic usage and adherence to medical guidelines.
Antibiotic Resistance

Antibiotic resistance is a phenomenon where bacteria evolve to withstand the effects of antibiotics. This resistance occurs naturally over time but is accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics in both human medicine and agriculture. The result is strains of bacteria that are no longer susceptible to standard treatments, complicating the management of infections.
The global health implications of antibiotic resistance are alarming. Resistant bacteria can spread across communities and borders, leading to outbreaks that are difficult to control. Efforts to combat resistance include promoting responsible antibiotic use, developing new antibiotics, and implementing infection control measures. The fight against antibiotic resistance requires a concerted effort from healthcare providers, policymakers, and the public alike.
Side Effects And Allergies
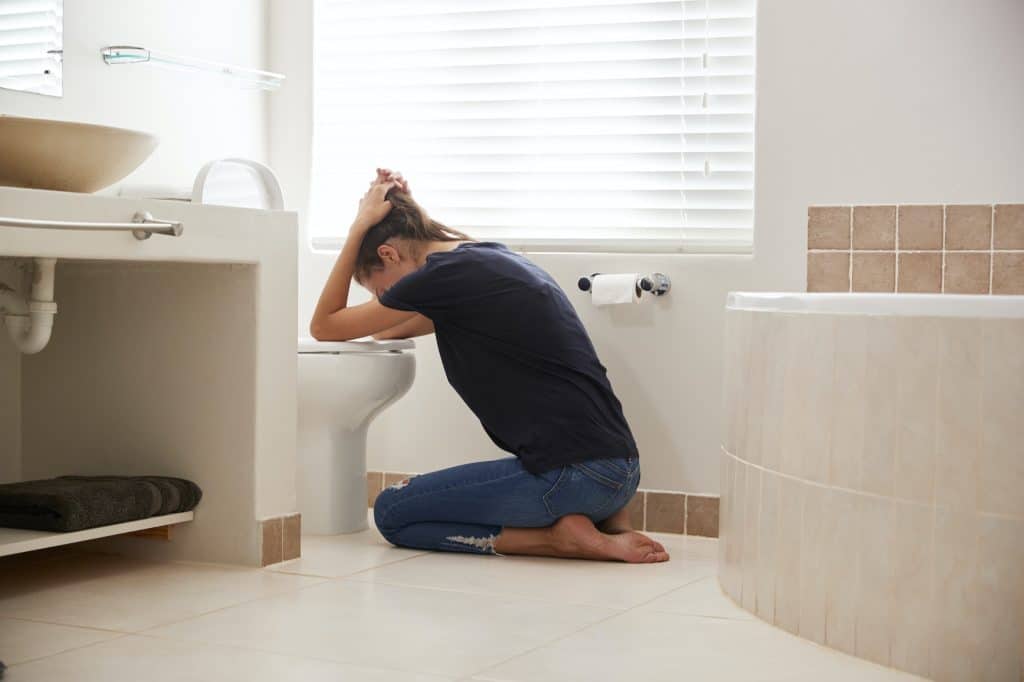

While antibiotics are essential in treating bacterial infections, they are not without side effects and potential allergic reactions. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and skin rashes, which are usually mild and temporary. However, more severe reactions can occur, particularly if antibiotics are misused or taken without proper medical supervision.
Allergic reactions to antibiotics, though rare, can be serious and even life-threatening. Symptoms may include hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing. It is crucial for patients to inform healthcare providers of any known allergies and to seek medical attention if an allergic reaction occurs. Understanding the potential risks and being vigilant about following medical guidance can mitigate these risks and ensure that antibiotics are used safely and effectively.
Antibiotics In Agriculture
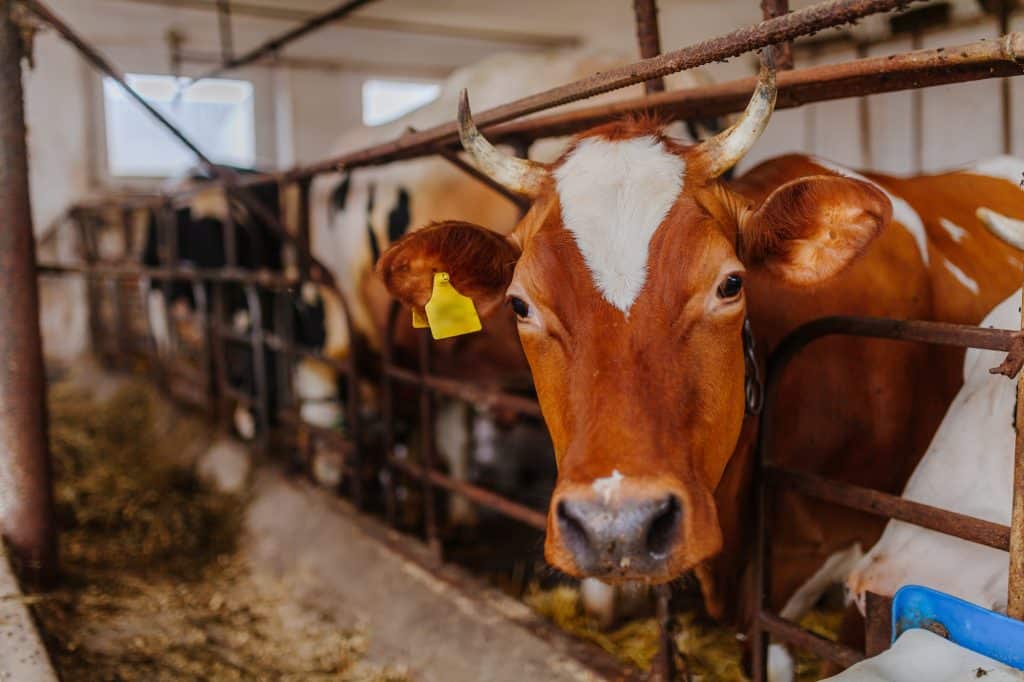

The use of antibiotics extends beyond human medicine into agriculture, where they are used to promote growth and prevent disease in livestock. This practice has become controversial due to its potential impact on human health. The widespread use of antibiotics in animals can lead to the development of resistant bacteria, which can then be transmitted to humans through the food chain.
In addition to livestock, antibiotics are also used in crop farming to combat bacterial diseases in plants. Regulatory measures and guidelines are in place to control the use of antibiotics in agriculture, but challenges remain. Balancing the benefits of antibiotics in food production with the potential risks requires careful consideration, ongoing research, and collaboration between farmers, regulators, and scientists.
Alternatives To Antibiotics
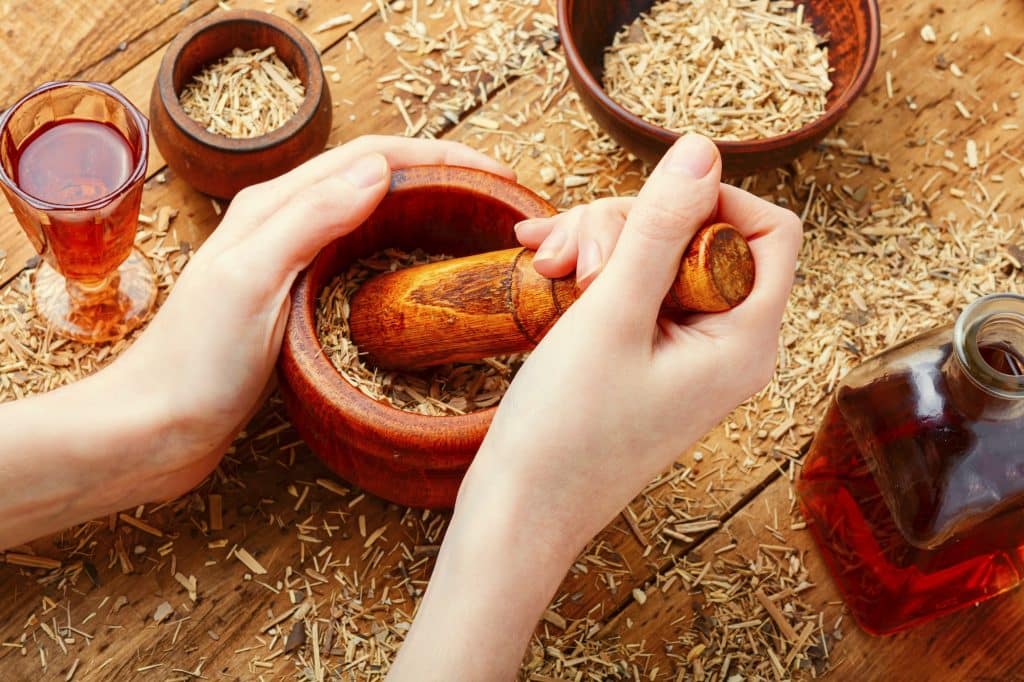

As antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern, the search for alternatives to traditional antibiotics has intensified. Research into novel treatments includes exploring substances with antimicrobial properties, such as certain metals, peptides, and even bacteriophages, which are viruses that attack bacteria. These alternatives aim to provide new ways to combat bacterial infections without contributing to resistance.
Herbal and natural remedies are also being investigated as potential alternatives to antibiotics. While some of these substances have been used in traditional medicine for centuries, scientific research is needed to validate their efficacy and safety. The pursuit of alternatives to antibiotics is a complex and vital area of research that holds promise for the future of medicine, potentially revolutionizing how infections are treated.
Proper Usage And Precautions
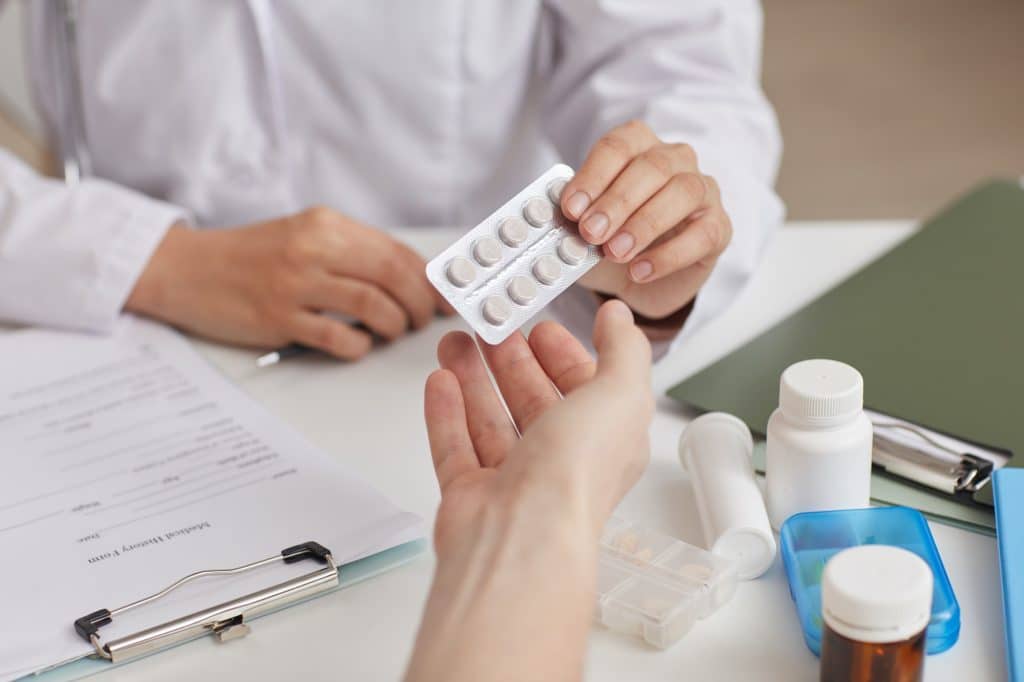

Proper usage of antibiotics is essential to their effectiveness and the prevention of resistance. This includes taking the prescribed dose at the right times, completing the full course of treatment, and never sharing antibiotics with others. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can lead to treatment failure and contribute to the development of resistant bacteria.
Precautions also extend to healthcare providers, who must prescribe antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary. Educating patients about the importance of following instructions and the potential risks of misuse is also crucial. The responsibility for proper antibiotic usage is shared between patients and healthcare providers, and adherence to these principles is vital for maintaining the efficacy of these life-saving drugs.
Know The Truth About Antibiotics
Antibiotics are a cornerstone of modern medicine, with a complex history, diverse types, and multifaceted applications. From their discovery to their role in agriculture, and from their misuse to the search for alternatives, antibiotics continue to be a subject of immense importance and intrigue. This post has explored various aspects of antibiotics, shedding light on lesser-known facts and emphasizing the need for responsible usage. The understanding and appreciation of antibiotics are essential for preserving their effectiveness and ensuring that they continue to serve humanity in the fight against bacterial infections.