Gingivitis is a common but often ignored form of gum disease that can have serious implications if not addressed early. It’s a condition that affects a significant portion of the population, yet many are unaware of its signs and symptoms. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing the progression of the disease and for maintaining overall oral health. By the end of this read, you’ll be well-equipped with the knowledge you need to identify and address the signs of gingivitis effectively.
Contents
What Is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums, primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque on the teeth and gum line. It’s the earliest stage of gum disease and is usually reversible with proper treatment. However, if left untreated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis. This advanced stage can lead to tooth loss and other complications.
Poor oral hygiene is the primary cause of gingivitis, as it encourages plaque to form on teeth. This plaque causes inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. Other contributing factors can include smoking, hormonal changes, and poor nutrition. Medical conditions such as diabetes can also make individuals more susceptible to gingivitis.
The Prevalence Of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is alarmingly common, affecting a large percentage of the global population. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly half of all adults in the United States have some form of gum disease. Gingivitis is the most prevalent form, making awareness and early intervention crucial. These statistics underscore the importance of maintaining good oral health.
While gingivitis can affect people of all ages, it is more common among adults. Certain demographics, such as pregnant women, are at higher risk due to hormonal changes. These hormonal shifts make the gums more susceptible to inflammation. Individuals with pre-existing conditions like diabetes are also more likely to develop gingivitis, emphasizing the need for these groups to be extra vigilant about their oral health.
Early Signs Of Gingivitis
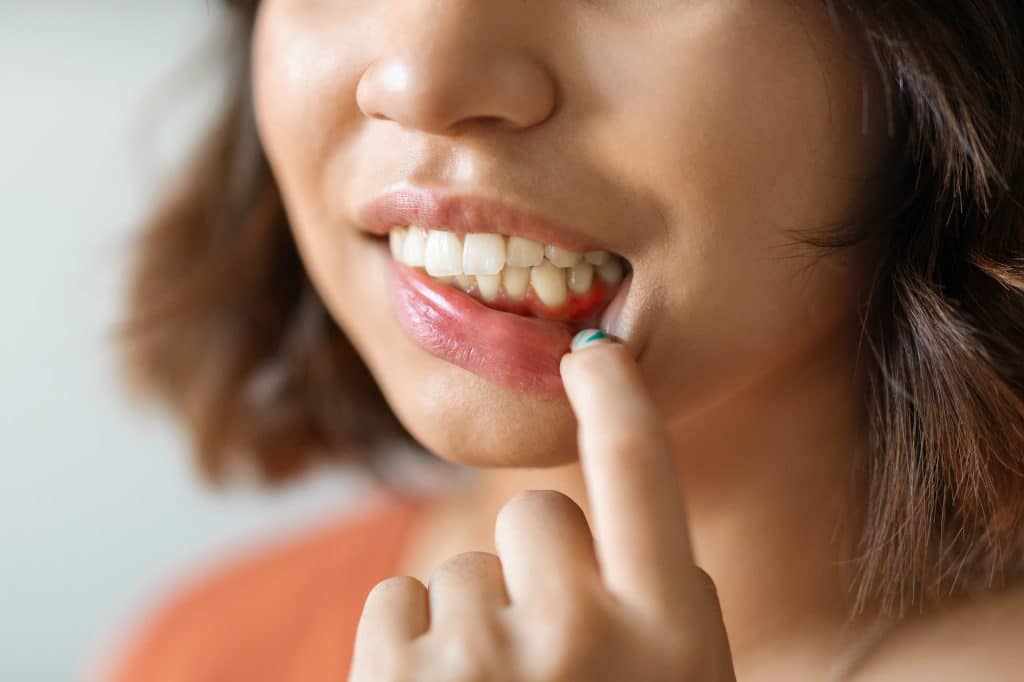

One of the first signs of gingivitis you may notice is a change in the color of your gums. Healthy gums are generally a pale pink, but when inflamed, they may appear redder than usual. This redness is often accompanied by a shiny or glossy appearance, which indicates inflammation. Both of these symptoms are early indicators that should not be ignored, as they suggest the need for immediate attention to prevent the condition from worsening.
Swollen gums are another early sign of gingivitis that should prompt immediate action. The gums may feel tender to the touch and may even appear puffy or distended. This swelling is a result of the body’s natural response to infection and is a sign that your gums are fighting off bacteria. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent the condition from progressing to more severe forms of gum disease, saving you from potential tooth loss and complicated treatments.
Advanced Symptoms
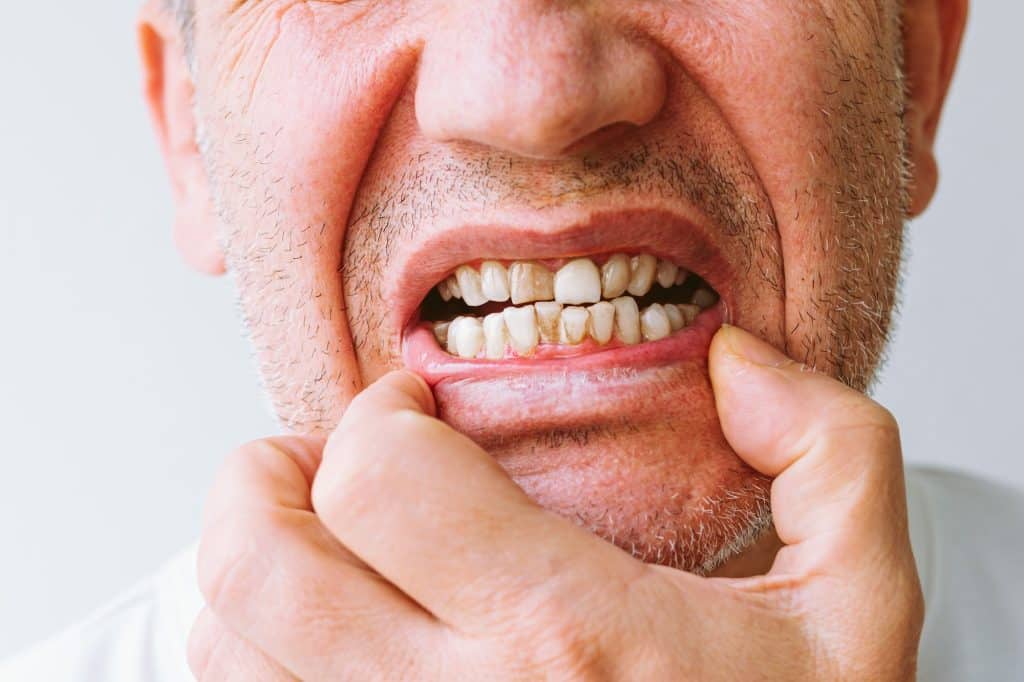
As gingivitis progresses, the symptoms can become more severe and noticeable. One such symptom is persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis. This isn’t the typical morning breath that most people experience; it’s a constant foul odor that doesn’t go away even after brushing or using mouthwash. The smell is due to the bacteria and decaying food particles trapped in the plaque and tartar on your teeth and gums. Another advanced symptom is the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums, which can trap food and plaque, exacerbating the condition.
Receding gums are another advanced symptom of gingivitis that should not be ignored. When gums recede, more of the tooth’s root becomes exposed, making teeth appear longer. This can lead to increased sensitivity, especially when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages. The exposure of the tooth root also creates more surface area for plaque and bacteria to build up, increasing the risk of further infection and complications.
Risk Factors
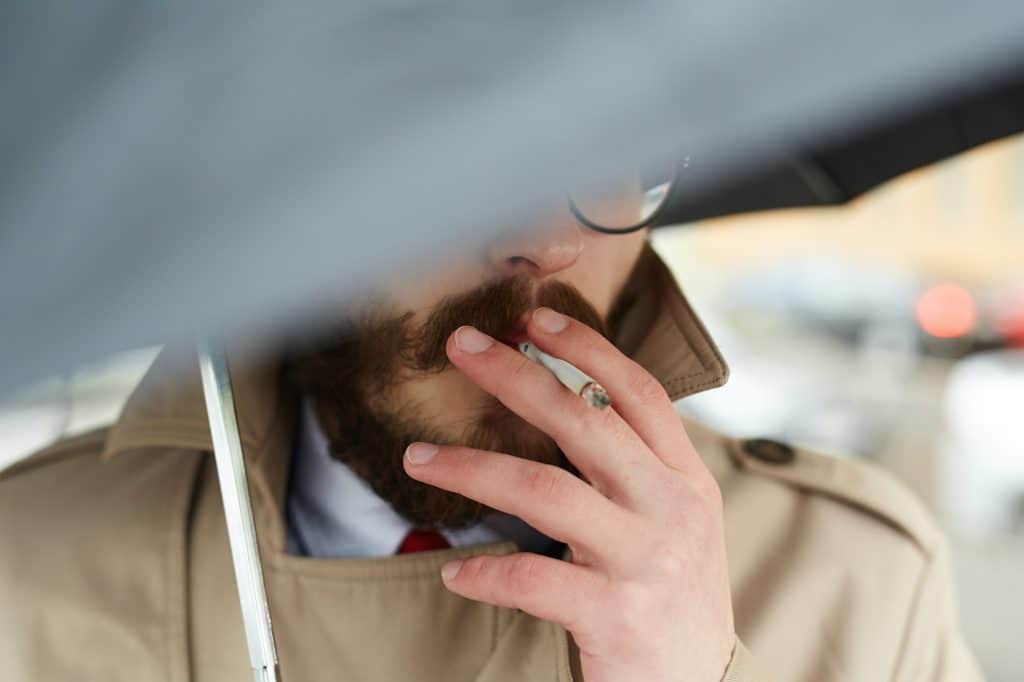

While poor oral hygiene is the most common risk factor for gingivitis, there are other elements that can increase your susceptibility to this gum disease. Smoking or using tobacco products is one such factor. The chemicals in tobacco can affect the health of your gums, making it easier for gingivitis to take hold. Additionally, medications such as anticonvulsants and certain antihypertensive drugs can affect gum health. Hormonal changes, particularly in women going through puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can also make gums more vulnerable to gingivitis.
Underlying health conditions can significantly contribute to the risk of developing gingivitis. For instance, diabetes affects your body’s ability to use blood sugar and can lead to higher levels of sugar in the saliva, providing a breeding ground for bacteria. Stress, which weakens the immune system, can also be a contributing factor, as it makes it harder for the body to fight off infection. Poor nutrition, including vitamin C deficiency, can compromise the health of your gums, making them more susceptible to infection.
Diagnosis

If you suspect you have gingivitis, the first step is to consult a dentist for a thorough examination. During the check-up, the dentist will examine your gums for signs of inflammation, redness, and swelling. They may also measure the pockets around your teeth using a special instrument. X-rays may be taken to check for bone loss around the teeth, which is a sign of more advanced gum disease. A dental professional may also ask about your medical history and any symptoms you’ve been experiencing.
In some cases, you may be referred to a periodontist, a dentist who specializes in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of periodontal disease. The periodontist may conduct further tests, such as taking a small sample of your gum tissue for analysis. This can help determine the type and extent of the infection. Blood tests may also be conducted to rule out other medical conditions that could be contributing to your symptoms.
Treatment Options
Treating gingivitis is crucial for preventing its progression to more severe forms of gum disease. The first line of treatment usually involves a professional dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar build-up. This is often followed by a regimen of oral hygiene instructions, including proper brushing and flossing techniques. Over-the-counter antiseptic mouthwashes can also be effective in reducing plaque and gingivitis when used in conjunction with regular brushing and flossing. Your dentist may also recommend specific toothpaste designed to fight plaque and gingivitis.
In more severe cases, medication may be prescribed to control the infection and inflammation. Antibiotics, either topical or oral, are commonly used to treat bacterial infections in the gums. In some instances, surgical procedures like scaling and root planing may be necessary to remove deep pockets of plaque and tartar. Home remedies, such as saltwater rinses, can also provide temporary relief from symptoms but should not replace professional medical advice and treatment.
Prevention

Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to gingivitis. The cornerstone of prevention is maintaining good oral hygiene. This involves brushing your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove plaque from areas your toothbrush can’t reach, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also essential for keeping your gums healthy. During these visits, your dentist can identify early signs of gingivitis and take preventive measures before the condition worsens.
Diet also plays a significant role in the prevention of gingivitis. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, can help strengthen your gums and teeth. Foods high in sugar and carbohydrates should be consumed in moderation as they can contribute to plaque formation. Drinking plenty of water helps to wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of plaque build-up. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, can also significantly reduce your risk of developing gingivitis.
When To See A Dentist
Knowing when to consult a dentist can make a significant difference in the effective treatment of gingivitis. If you notice any of the early or advanced symptoms discussed in this post, it’s crucial to schedule a dental appointment as soon as possible. Early intervention can prevent the condition from progressing to more severe forms of gum disease, saving you from potential tooth loss and complicated treatments. Don’t ignore signs like bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or changes in the color or texture of your gums.
Emergency situations require immediate attention. If you experience severe pain, excessive bleeding, or signs of infection such as pus, you should seek emergency dental care. These could be indicators of an advanced stage of gum disease or another serious dental condition. Waiting too long to seek professional help can lead to complications that are more difficult and costly to treat. Therefore, it’s better to err on the side of caution and consult a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The Consequences Of Ignoring Gingivitis
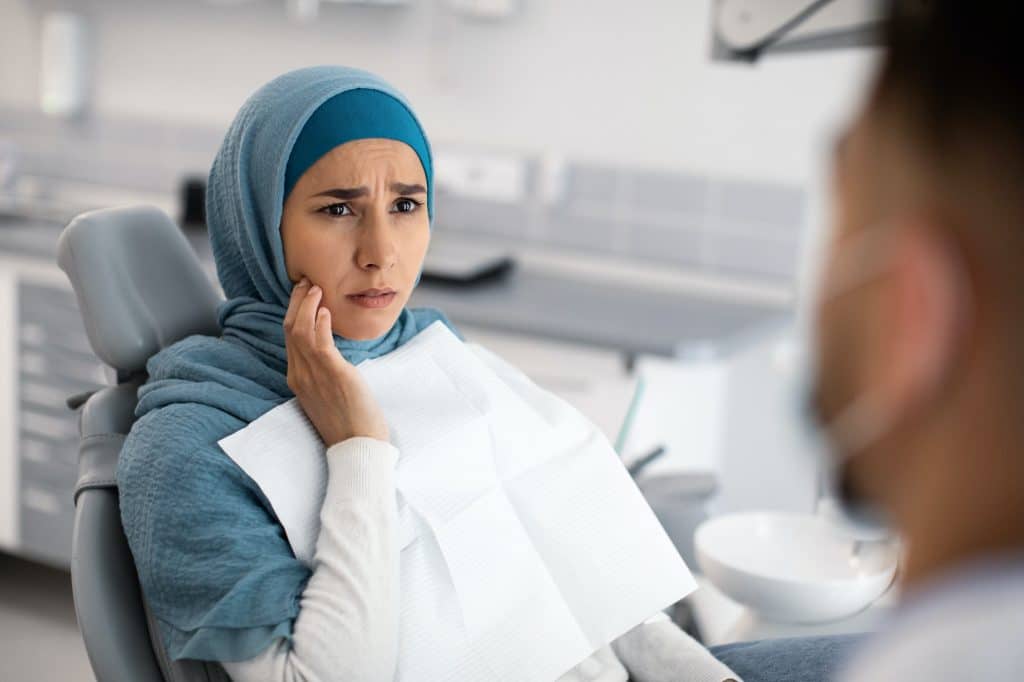

Ignoring the signs and symptoms of gingivitis can lead to severe consequences. One of the most significant risks is the progression to periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease. Periodontitis can lead to the loss of teeth and the deterioration of the jawbone. It can also cause gum abscesses and increase the likelihood of plaque entering the bloodstream, posing risks to your overall health.
Untreated gingivitis doesn’t just affect your oral health; it can have systemic implications as well. Research has shown a link between gum disease and other health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. The bacteria from your mouth can enter the bloodstream and affect other parts of the body, making it crucial to address gingivitis as part of your overall health and well-being.
Be Aware Of The Affects Of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common yet often overlooked condition with serious implications if left untreated. Early detection is crucial to prevent its progression to more severe forms of gum disease. This post has equipped you with essential knowledge about its signs, risk factors, and treatment options. If you experience any symptoms, consult a dental professional promptly to safeguard your oral and overall health.