Toenail fungus, scientifically known as Onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects countless individuals worldwide. It’s not just a cosmetic concern; if left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications. Early identification and prompt treatment are crucial to managing and eradicating this pesky problem. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding, identifying, and addressing toenail fungus to ensure you can take the best possible care of yourself.
Contents
What Is Toenail Fungus?
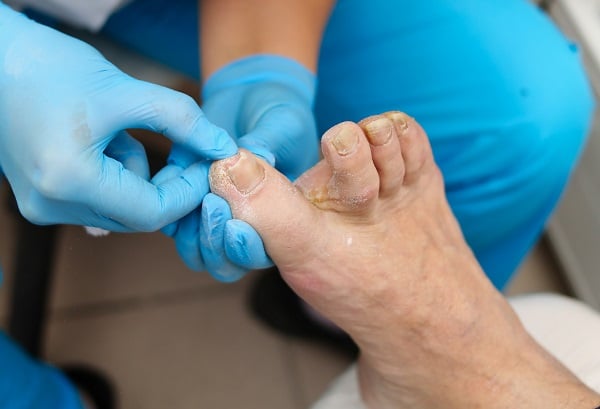
Toenail fungus is an infection that occurs when fungi invade the nail. This invasion usually happens through a small cut or break in the nail or surrounding skin. The condition is characterized by a yellowish or whitish discoloration, and as it progresses, the nail can become thick, brittle, and distorted. While many might dismiss it as a mere cosmetic issue, it’s essential to understand that untreated toenail fungus can lead to more severe complications.
The prevalence of toenail fungus is quite high, with millions of cases reported annually. It’s more common in adults, especially those over 60, but it can affect individuals of all ages. The condition can be persistent, and recurrence is common even after successful treatment. Therefore, understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step toward effective management.
Causes Of Toenail Fungus
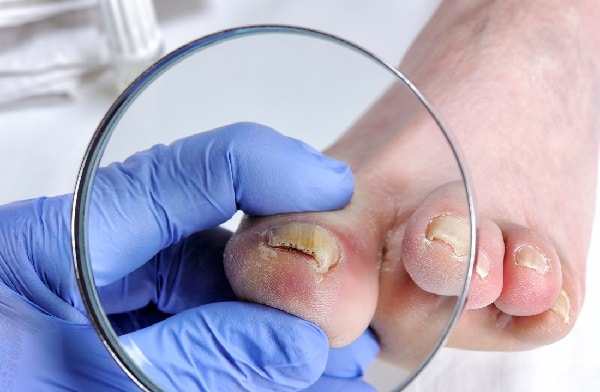
The primary culprits behind toenail fungus are specific types of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. Dermatophytes are the most common fungi responsible for toenail infections. They thrive in warm, moist environments, making places like public swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms potential hotspots for infection.
Environmental factors also play a significant role in the development of toenail fungus. Continuously wearing damp shoes or socks can create an ideal environment for fungi to thrive. Additionally, minor injuries to the nail, such as small cuts or even a slight separation between the nail and nail bed, can provide an entry point for these organisms. Once they gain access, they can quickly establish themselves, leading to the visible symptoms of the infection.
Common Symptoms
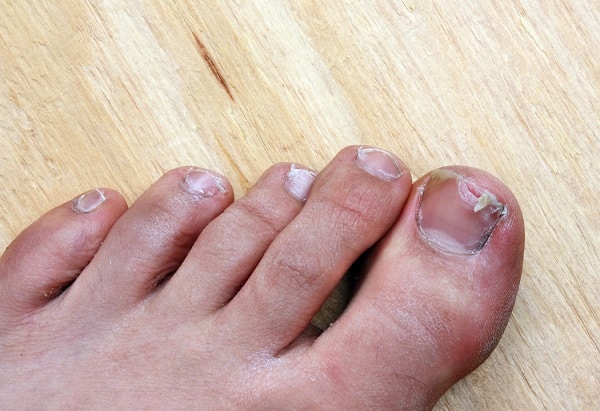
One of the first signs of toenail fungus is a noticeable change in the nail’s color. It might start as a small, white, or yellow spot under the tip of the toenail. As the fungal infection goes deeper, it can cause the nail to discolor entirely, thicken, and develop crumbling edges. This can be an unsightly condition, often leading to self-consciousness in individuals.
In more advanced cases, the symptoms become more pronounced. The nail can become distorted in shape, emitting a slightly foul odor. Pain can also be a symptom, especially when wearing shoes or walking. In some instances, the nail might separate from the nail bed, a condition known as onycholysis. Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
Risk Factors

Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing toenail fungus. Age is a significant risk factor, with older adults being more susceptible due to reduced blood flow to the toes and slower-growing nails. This makes it easier for the fungus to establish itself and spread. Additionally, as you age, you may have more years of exposure to fungi, increasing the chances of infection.
Another common risk factor is having sweaty feet. Fungi thrive in moist environments, so consistently damp feet can provide an ideal breeding ground. Specific footwear choices, such as tight-fitting shoes that constrict the toes or shoes made of materials that don’t allow feet to breathe, can also contribute to the development of toenail fungus. Other conditions, like athlete’s foot, can increase the risk, as can a weakened immune system which might not effectively combat the invading fungi.
Prevention Tips

Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to toenail fungus. One of the most effective preventive measures is maintaining proper foot hygiene. This includes washing feet regularly and ensuring they are thoroughly dry before wearing socks or shoes. It’s essential to focus on the spaces between the toes, as moisture can easily get trapped there.
Choosing the proper footwear is equally crucial. Shoes that are made of breathable materials can help in reducing moisture build-up. Rotating between different pairs of shoes and allowing them to air out can also be beneficial. Furthermore, it’s advisable to avoid walking barefoot in public places like gyms, showers, or swimming pools. Finally, using antifungal sprays or powders can act as an additional protective layer against potential fungal invaders.
Diagnosis
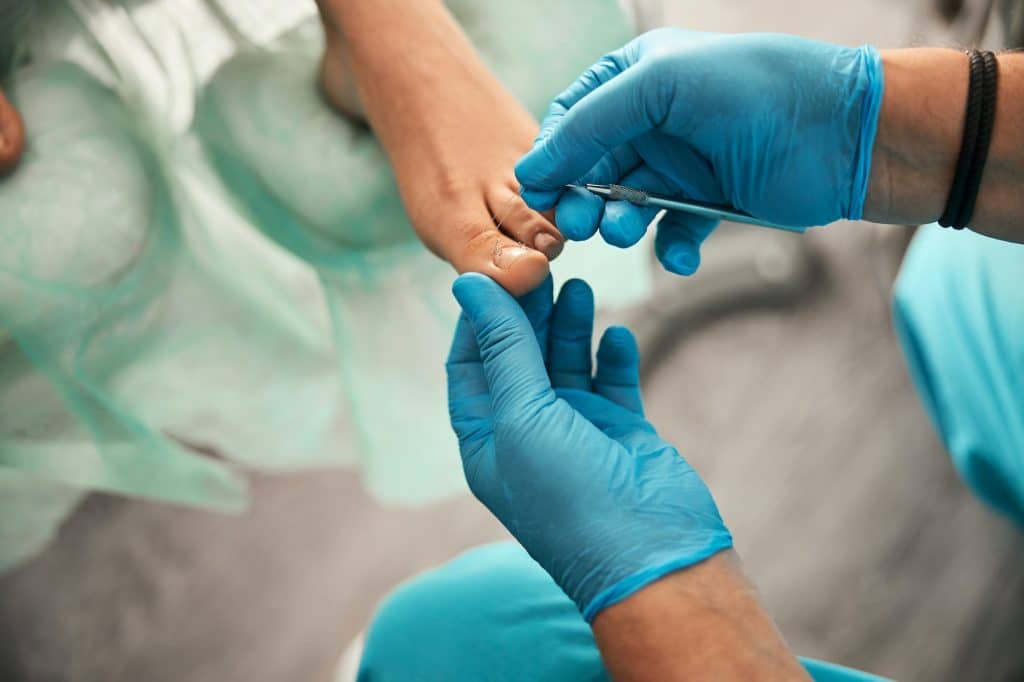
If you suspect you have toenail fungus, it’s essential to get a proper diagnosis. A healthcare professional can often identify toenail fungus by merely examining the affected nail. They might observe the characteristic discoloration, thickening, and other changes that indicate the presence of a fungal infection. However, visual inspection alone might not always be conclusive.
For a definitive diagnosis, a doctor might take nail clippings or scrapings from underneath the nail. These samples are then sent to a lab to identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection. This step is crucial, as the treatment approach might vary depending on the particular fungus involved. A precise diagnosis ensures that the treatment is targeted and effective.
Treatment Options
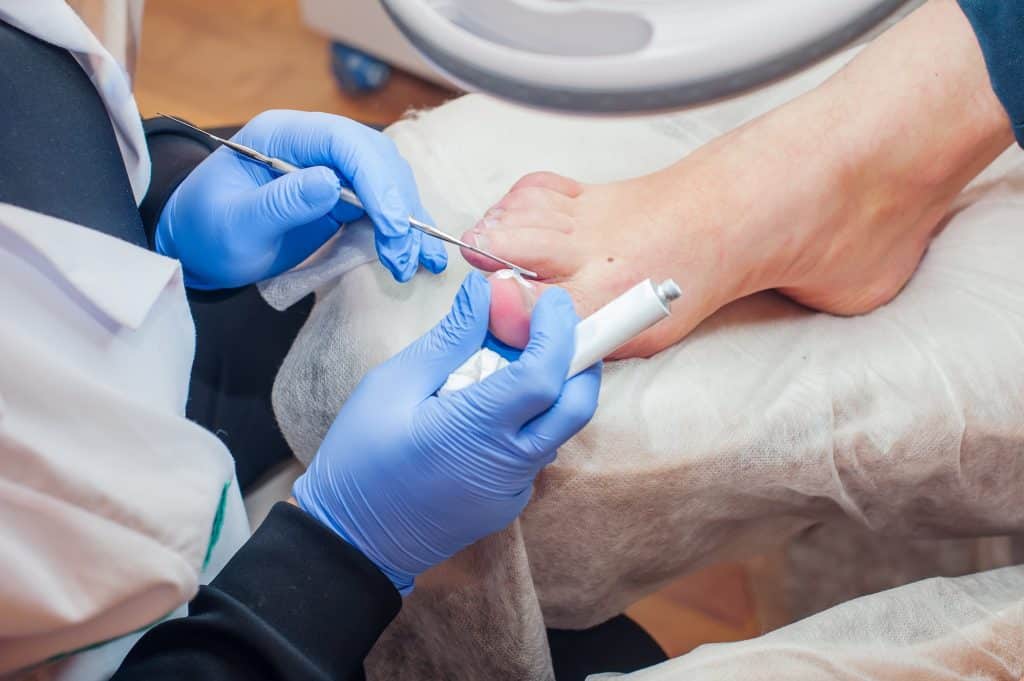
Once diagnosed, it’s essential to start treatment promptly to prevent the fungus from spreading or causing further complications. Over-the-counter antifungal creams and ointments can be effective for milder cases. These are applied directly to the nail and surrounding skin, often over several weeks, to combat the fungal infection.
For more severe or persistent infections, a doctor might prescribe oral antifungal medications. These drugs help the new nail grow free of infection, slowly replacing the infected part. However, they can have side effects and might not be suitable for everyone. In extreme cases, surgical removal of the nail might be necessary. Another emerging treatment option is laser therapy, which targets and kills the fungi without damaging the surrounding tissue.
Home Remedies
Many individuals turn to home remedies as a first line of defense against toenail fungus, either due to their preference for natural treatments or as an adjunct to conventional therapies. One popular remedy is Vicks VapoRub, a mentholated ointment. Some studies suggest that its ingredients, including camphor and eucalyptus oil, might be effective against certain types of fungi. However, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Another commonly cited home remedy is tea tree oil, known for its antifungal and antiseptic properties. Similarly, oregano oil, rich in thymol, has shown potential in combating certain fungi. Snakeroot extract, derived from the sunflower family, is another natural product that has demonstrated antifungal capabilities in some studies. While these remedies can be beneficial, it’s essential to approach them with caution. Not all are backed by robust scientific evidence, and some might cause skin irritation or allergic reactions.
Final Thoughts On Tackling Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus, while common, shouldn’t be taken lightly. Beyond the cosmetic concerns, it can lead to discomfort, pain, and further complications if not addressed promptly. Recognizing the signs, understanding the risk factors, and taking preventive measures are crucial steps in managing this condition. While there are various treatment options available, from over-the-counter solutions to prescribed medications and home remedies, it’s essential to choose the one that’s most suitable for your specific situation. Always consult with a healthcare professional to ensure you’re taking the right approach. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to effectively dealing with toenail fungus.